Get A Quote
Rotational Molding: A Complete Guide to the Process, Benefits, and Applications
Rotational molding, often referred to as rotomolding, is a highly versatile manufacturing process used to produce hollow plastic parts and products. Thanks to its ability to produce seamless rotational molding products with uniform wall thickness, rotational molding is widely applied across industries such as automotive, agriculture, marine, and industrial manufacturing.
If you want to understand how rotational molding works, what makes it different from other plastic molding processes, and why so many manufacturers rely on it, this complete guide covers everything you need to know.
What is Rotational Molding?
Rotational molding is a plastics manufacturing process that involves heating and rotating a mold filled with plastic resin to create hollow products. Unlike injection molding or blow molding, rotomolding does not require high pressure. Instead, the process relies on heat and bi-axial rotation to evenly distribute the resin along the inside walls of the mold, resulting in durable, hollow structures.
Key Steps in the Rotational Molding Process
The rotational molding process can be broken down into four key stages:
Loading the Mold with Resin
A pre-measured amount of plastic resin—most commonly polyethylene in powder form—is placed into a hollow mold. These molds are usually made from aluminum or steel and are precisely designed to match the final shape of the rotational molding product.Heating and Rotating the Mold
Once the resin is loaded, the mold is heated in an oven while it rotates around two perpendicular axes. This rotation ensures that the melted plastic evenly coats the interior surface of the mold, forming the desired shape.Cooling the Mold
After the heating phase, the mold is transferred to a cooling station. The mold continues to rotate as it cools, solidifying the plastic and maintaining the shape of the part. Water or air is used to accelerate cooling.Unloading the Final Product
Once the mold has cooled, it is opened, and the newly formed hollow part is removed. The final product requires minimal finishing, as the rotational molding process leaves no seams or weld lines.
Benefits of Rotational Molding
Compared with other plastic manufacturing methods, rotational molding offers several key advantages:
Cost-Effective for Low-Volume Production
One of the primary benefits of rotomolding is its cost-efficiency for low to medium production runs. Molds are relatively inexpensive compared to injection molding, making it an attractive option for smaller batches.Uniform Wall Thickness
The bi-axial rotation ensures that the plastic coats the entire mold uniformly, resulting in consistent wall thickness without weak points. This makes rotational molding ideal for producing durable, stress-resistant parts.Design Flexibility
Rotational molding allows for complex shapes and design features such as undercuts, inserts, and varying wall thicknesses in a single part. Manufacturers can also easily incorporate colors, textures, and logos directly into the product.Minimal Material Waste
Rotomolding is an environmentally friendly process because there is very little material waste. The resin not used in the molding process can be collected and reused in subsequent runs, making it an efficient and sustainable option.Durability and Strength
Products made through rotational molding are typically stronger and more durable than those made through blow molding or thermoforming due to the consistent material distribution. Rotomolded items can also withstand harsh environmental conditions.
Applications of Rotational Molding
Rotational molding is a highly adaptable process used across a variety of industries. Some of the most common applications include:
Industrial and Agricultural Equipment
Rotomolded components are widely used in industrial and agricultural equipment because of their durability and resistance to extreme temperatures and chemicals. Common products include tanks, containers, and machinery parts.Automotive Parts
The automotive industry benefits from rotomolded components due to their lightweight yet strong nature. Common examples include dashboards, bumpers, and fuel tanks.Outdoor Furniture and Playground Equipment
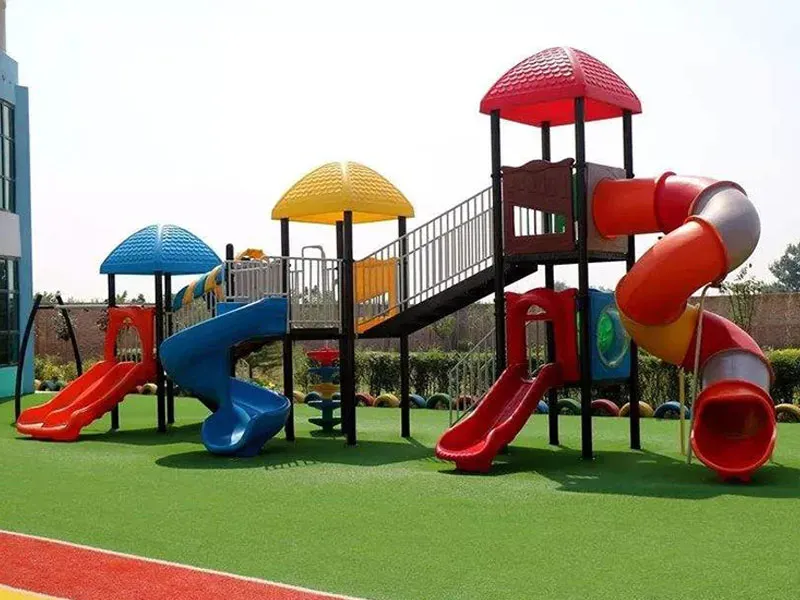
Outdoor furniture and playground equipment are often produced through rotational molding because the process allows for large, seamless structures that are weather-resistant and durable.Marine and Boating Components
Rotomolding is used to create various marine products, including water tanks, buoys, and seating, because of its ability to produce hollow, waterproof components.Storage Containers
Rotational molding is ideal for creating large storage containers like trash bins, water tanks, and bulk handling units due to its capacity to make durable, lightweight, and leak-proof items.
Rotational Molding vs. Injection Molding: Which is Better?
A common question manufacturers ask is whether rotational molding or injection molding is better for their needs. The answer depends on the specific requirements of the project.
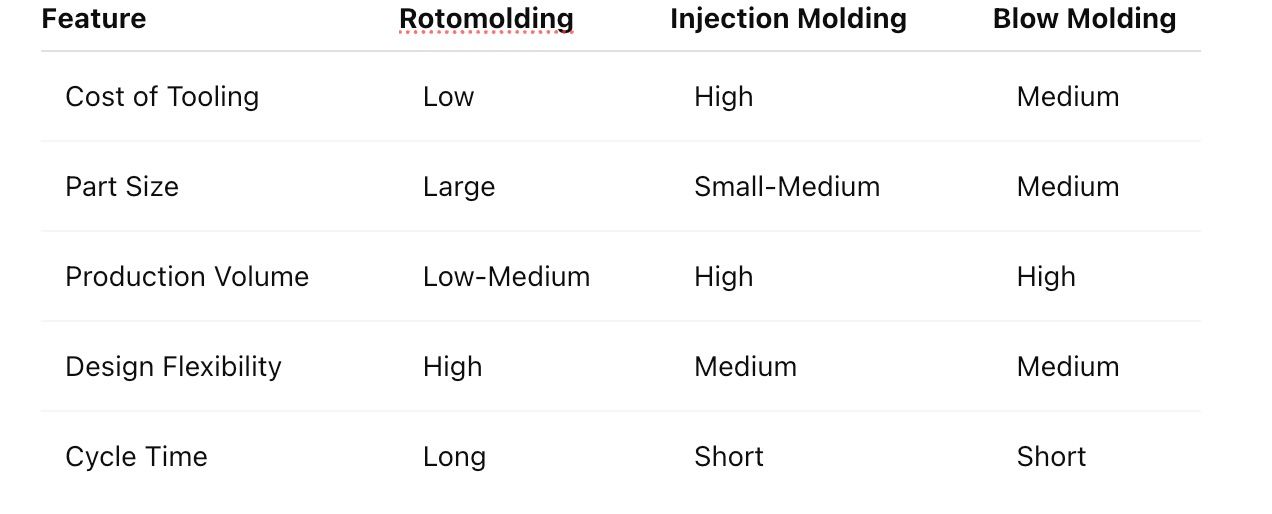
Rotational Molding is better for producing large, hollow items with uniform wall thickness. It’s also more cost-effective for small to medium production runs due to lower mold costs. However, the cycle times are longer, and it’s not suitable for high-volume production.
Injection Molding is ideal for high-volume production of solid parts with intricate details. While the upfront mold costs are higher, the process is faster, making it more cost-effective for large-scale manufacturing. Injection molding is not typically used for hollow parts or large items.
Each process has its strengths and weaknesses, and the best method depends on the design, material, and production needs.
Rotomolding vs Other Plastic Molding Processes
Here’s how rotomolding compares to other methods:
Manufacturers may encounter certain process-related issues such as uneven thickness, long cycle times, or cooling challenges. For a deeper look at these issues and proven solutions, you can read this detailed guide: Common Challenges in Rotational Molding and How to Overcome Them
Design Tips for Rotational Molding
Designing for rotomolding takes a little know-how. Here are some tips:
- Uniform Wall Thickness – Keep walls even to prevent weak spots.
- Avoid Sharp Corners – Use rounded edges for better material flow.
- Draft Angles – Add slight angles to help release parts from molds.
- Ribs and Bosses – Reinforce parts without adding thickness.
- Threaded Inserts – Plan for metal inserts during the molding stage.
Good design reduces cost, shortens production time, and improves product performance.
Environmental Impact of Rotomoldin
Rotational molding is considered environmentally friendly for several reasons:
- Low Waste – No runners or sprues like injection molding.
- Recyclable Materials – Most resins used are recyclable.
- Durable Products – Long-lasting parts reduce replacement needs.
- Energy Efficient – Newer ovens use less energy and emit fewer pollutants.
As sustainability becomes more important, rotomolding offers a responsible choice for manufacturers.
Why Choose Benfan for Your Rotational Molding Needs?
At Benfan, we specialize in advanced rotational molding equipment and customized manufacturing solutions. Our expertise in rotational molding of plastics allows us to support a wide range of industries with reliable, high-performance machinery.
We pride ourselves on offering:
- High Precision Molds: Custom-designed molds that ensure uniform thickness and durability in every product.
- Comprehensive Services: From design to production, we support you through every step of the manufacturing process.
- Sustainable Manufacturing: Our rotational molding processes are designed to minimize waste and maximize material efficiency.
Whether you produce industrial tanks, automotive parts, or consumer products, we delivers dependable solutions tailored to your needs.
Conclusion
Rotational molding of plastics is a flexible, cost-effective, and durable manufacturing solution for producing hollow plastic components. With advantages such as uniform wall thickness, design freedom, and minimal waste, rotational molding continues to be a preferred choice for manufacturers worldwide.
For businesses seeking reliable, high-quality rotational molding products, investing in the right equipment and expertise makes all the difference—and that' s where Benfan stands out.